View the Use of Third-Party Software or Websites disclaimer.
Western Digital Support cannot help with third-party software or hardware.
Description
Poor or slow speeds can be caused by:
- Third-party hardware, adapter, docking station, or hub.
- Host device port speed.
- Format and file system.
- Directory with lots of small files.
- Deeply nested directory.
- USB cable too long.
- USB garbage collection.
- Not enough free space on the drive.
- Connected to slower USB port.
- The host does not have enough cache.
- The cache is not optimized.
- To many background programs.
- Multiple connections to the computer.
- Outdated drivers.
 |
WD external drives don't support UASP (USB Attached SCSI Protocol) except for the ArmorATD model. |
Resolution
USB Standard and Speeds
| Version | USB Interface Speeds | Ports |
|---|---|---|
| SUPERSPEED USB 20Gbps USB 3.2 (Gen 2x2) |
20 Gb/s (2500 MB/s) |
USB Type-C, USB Type-A, etc. |
| SUPERSPEED USB 10Gbps USB 3.2 (Gen 2), USB 3.1 (Gen 2) |
10 Gb/s (1250 MB/s) |
USB Type-C, USB Type-A, etc. |
| SUPERSPEED USB 3.2 (Gen 1), USB 3.1 (Gen 1), USB 3.0 |
5 Gb/s (625 MB/s) |
USB Type-C, USB Type-A, etc. |
| HI-SPEED USB 2.0 |
480 Mb/s (60 MB/s) |
USB Type C, USB Type-A, etc. |
| USB 1.1 | 12 Mb/s (1.5 MB/s) |
USB Type-A, USB Type-B, etc. |
Need more help?
Answer ID 5043: USB Interface Standards and Theorectical Speeds
Host Device USB-C Performance Specs
The speed of a drive depends on the port used.
Some systems have USB-C ports that work with different USB drives.
Solution: Check the host device to confirm specs of the USB-C port.
Performance Best Practices
- Directory and File Sizes (Lots of small files)
The total amount of data on a disk and the size of each file can result in slower speeds.
Information: A large number of files saved in a single directory will transfer faster than the same number of files spread across multiple directories.
 |
1 TB of large files will transfer much faster than 1 TB of millions of small files. |
- Windows and macOS File System
Drives are formatted as NTFS, FAT32, exFAT and HSF+. File systems like NTFS on Windows and APFS on macOS perform better than exFAT, FAT32 and HSF+
Solution: Format the drive with the native OS file system.
-
- Windows: format as NTFS
- macOS: format as APFS
Need more help?
- Encryption
Using encryption will cause slower read/write speeds.
Solution: Use a file system that does not encrypt data.
Turn off app level encryption.
My Book, My Book Duo, WD Backup Drive Desktop, and easystore Desktop use hardware encryption.
This cannot be turned off.
Need more help?
Answer ID 1837: WD External Drive Hardware Encryption Compatibility Matrix
- Windows Write Caching
Some drives need this turned on to get the best results.
This improves speeds by collecting commands sent to the drive.
IMPORTANT:
Loss of data can occur when Write Caching is turn on.
It can happen during data transfer if there is a sudden loss of power or hard shutdown of the computer.
Need more help?
Turn on write caching.
- Connect the drive.
- Press the Windows Key + X.
Click Device Manager. - Expand Disk Drives.
Right-click the drive.
Click Properties.
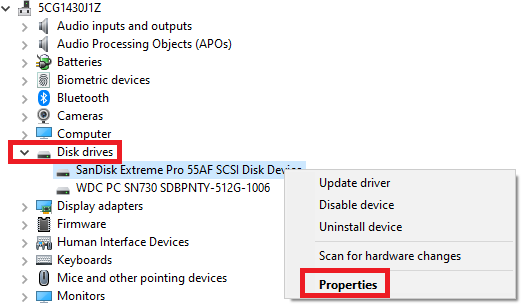
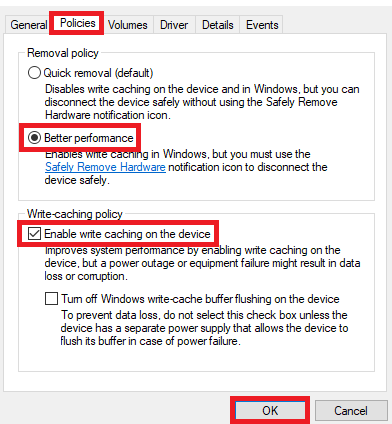
- Click Policies.
Click Better performance.
Click Enable write caching on the device.
Click OK.
- Windows 10 Real Time Protection
Doing a scan with this tool may cause slow speeds.
Solution: For a short time disable this tool.
Need more help?
Microsoft Article: Turn off antivirus protection in Windows Security
- Connect to a Different Computer
Slow speed may be caused by the computer.
Solution: Test the drive on another one.
- USB Hubs and Extension Cables
These can slow the drive speed.
Solution: Connect the drive directly into the host system.
- USB Port and Cable
Slow speeds can be caused by plugging into a slow or faulty USB port.
Solution:Use a high quality USB cable.
- USB Garbage Collection
This can cause slow or delayed speed on some drives.
It is used to free up flash memory space making the drive work good over time.
Solution: Let the process run.
- Confirm USB Type used by USB-C Port
Different types of USB use the USB-C port.
Solution:Confirm USB-C speeds offered by the systems USB-C port.
Contact the computer or motherboard maker for support.
- Drive Space Available
Performance can decrease when drives are close to capacity.
Solution: Make sure the drive has 10% to 15% space free for best results.
- Laptops and Portable Computers
Make sure the computer has at least a 75% charged battery or is plugged in.
Solution: Adjust the power mode or Energy Saver Settings.
- System Memory
Small amounts of memory may not have enough resources to process data. This can result in slow backups.
Solution: Stop apps and software that use high memory.
- Computer in use during Speed Tests
Using the computer when running a speed test can cause higher than normal CPU and memory.
Solution: DO NOT use the computer during these tests.
- Fragmented Disk
This may cause slow disk read.
Solution: Defragment the disk.
Need more help?
- Microsoft Article: Run the System File Checker tool.
- Microsoft Article: Defragment your Windows 10 PC
- Apple Article: How to repair a Mac disk with Disk Utility
- Anti-Virus, Anti-Malware and End Point Protection Software
These tools scan incoming TCP/UDP packets which cause slower data transfer rates.
Solution: Stop these softwares when moving data.
Turn back on when complete.
- Infected Computer
A computer with virus or malware may cause slow speeds.
Solution: Make sure that the system is virus, trojan, and malware free.
- Microsoft Article: Change the power mode for your Windows PC
- Apple Article: Change Energy Saver preferences on a Mac desktop computer
- System and BIOS
And outdated OS and BIOS can cause problems.
Solution: Update Windows or macOS.
Update the computer BIOS.
- RAID 0 vs RAID 1
RAID 0 offers the fastest read/write speeds but does not provide data protection like RAID 1.
Solution: Configure a device as RAID 0 for the best speeds.
- CPU (32 bit vs 64 bit)
Older 32 bit CPU systems may not have the power to handle modern technology.
Solution: Stop apps and software that use high CPU and memory.
- Outdated Motherboard Chipset or Drivers
These can affect system speeds.
Solution: Make sure that the motherboard chipset and drivers are up to date.
Contact the computer or motherboard maker for support.
Drive Diagnostic Tools
- Windows:
- Microsoft Article: Run the System File Checker tool
- Microsoft Article: Defragment your Windows 10 PC
- macOS:
- Western Digital Software: